Cloud Cost Report
The Q4 2023 Cloud Cost Report analyzes real-world data to quantify how cloud spending patterns are changing.
Fresh off the quarterly earnings for Microsoft, Google, and Amazon—where 'the period of massive optimization only and no new workloads has ended' (source)—we are releasing the Q4 2023 Cloud Cost Report, an analysis of cloud usage based on anonymized Vantage customer usage. Vantage is a cloud cost management and optimization platform, with a unique view into industry trends, thanks to tens of thousands of connected infrastructure accounts across 13 cloud providers. To discuss this report in more detail, join our growing Slack Community of over 1,000 engineering leaders, FinOps professionals, and CFOs. View past reports here.
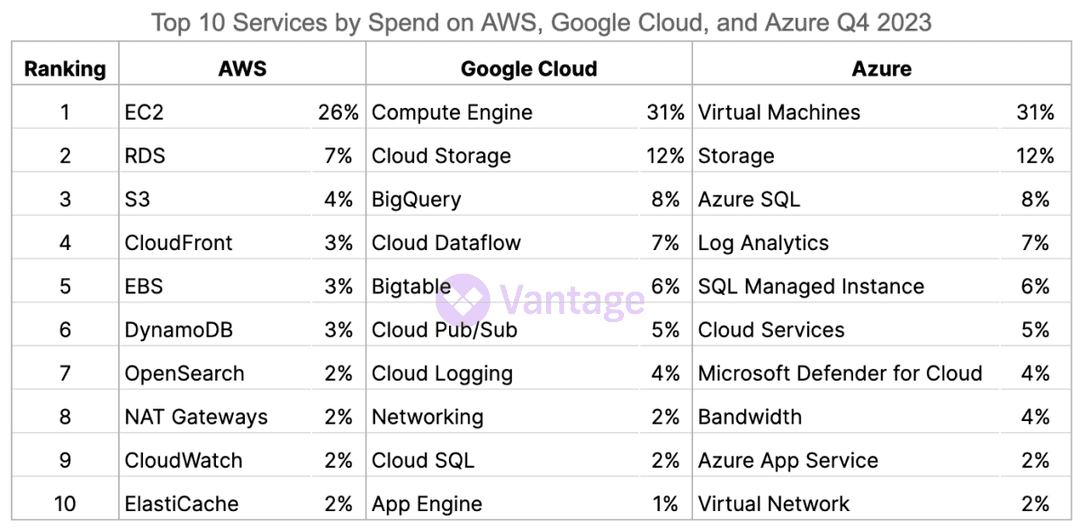
Top Services by Spend Across Clouds
Competition for marketplace share between cloud providers, such as the big three—AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, has never been higher. Azure is seemingly increasing their market share, and there are predictions that they will surpass AWS. In our data, the percentage spend of EC2 instances continues to decrease from previous quarters (previously at 42% during Q1), while Azure is increasing (up from 26% last quarter).
Some of the changes in the cloud landscape point to the rapid advancements in AI offerings in Q4. The growth of Azure can be largely attributed to its innovation in AI, with Azure OpenAI being hugely popular and considered the best by many. Amazon introduced its own widely anticipated Bedrock to compete. Microsoft's focus on service offerings may be giving them a leg up in the cloud wars.
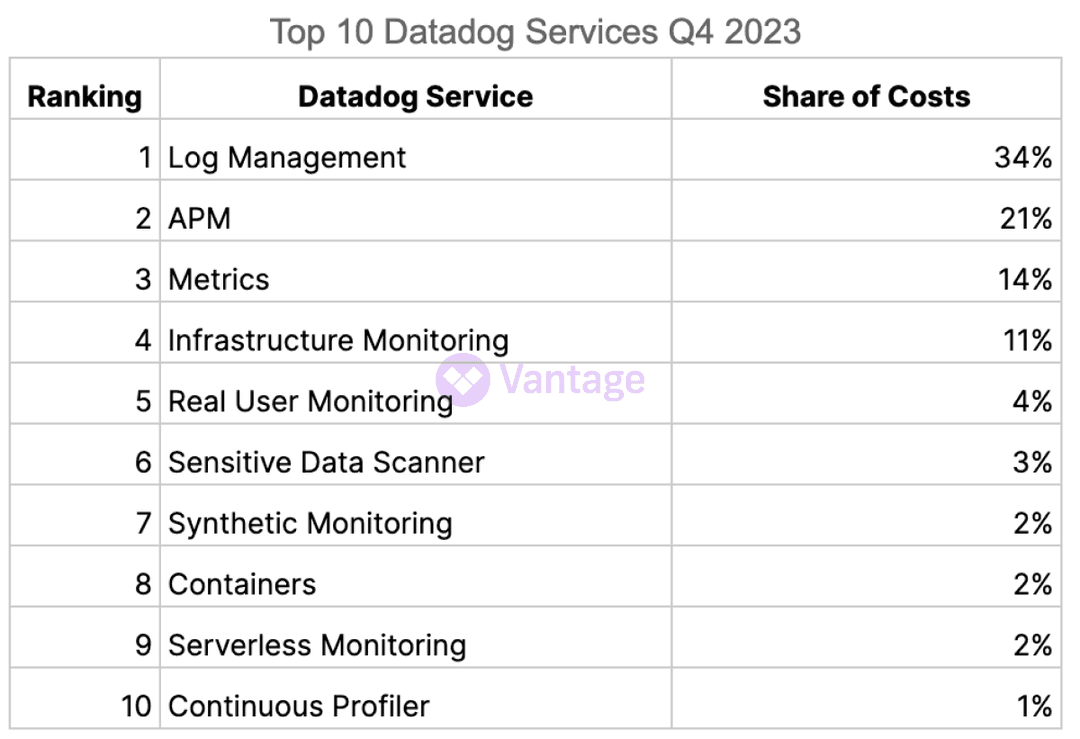
Core Datadog Workloads Expand
There are significant shifts in the Datadog spend landscape. Most remarkably, Log Management has increased 12% from Q3 and now accounts for over 1/3rd of the share of costs for Datadog services.
Along with the growth of cloud, observability has seen massive expansion in recent years. Datadog customers should keep in mind that they can lock in committed use discounts as they expand their usage of the platform. Vantage also launched support for usage attribution tags on Datadog last year, which are helpful for tying observability costs to core infrastructure spend.
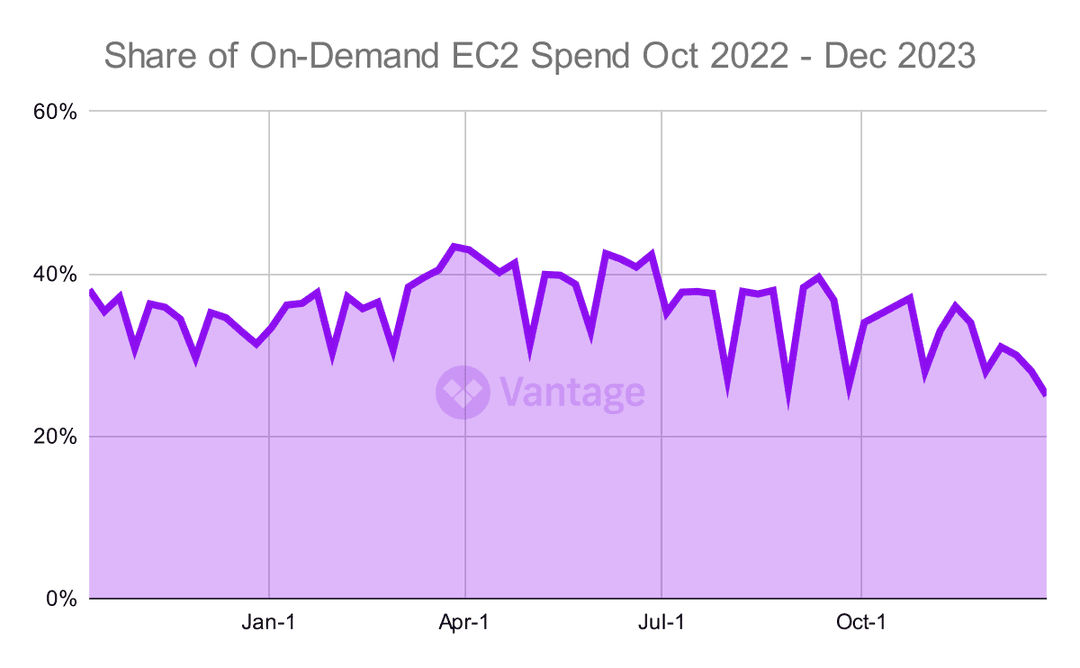
EC2 On-Demand Spend Drops to New Lows
On-Demand spend drops to new lows this quarter, driven by recent developments in the world of Reserved Instances (RIs). During December, the year ended with the percentage of On-Demand spend at 25%. That is the lowest in all of 2023.
Earlier this year, AWS disallowed the transfer of discounted RIs, affecting enterprise customers and pushing more teams to Savings Plans. See below in the report for more detail on the mix of RIs and spot instances that companies are turning to.
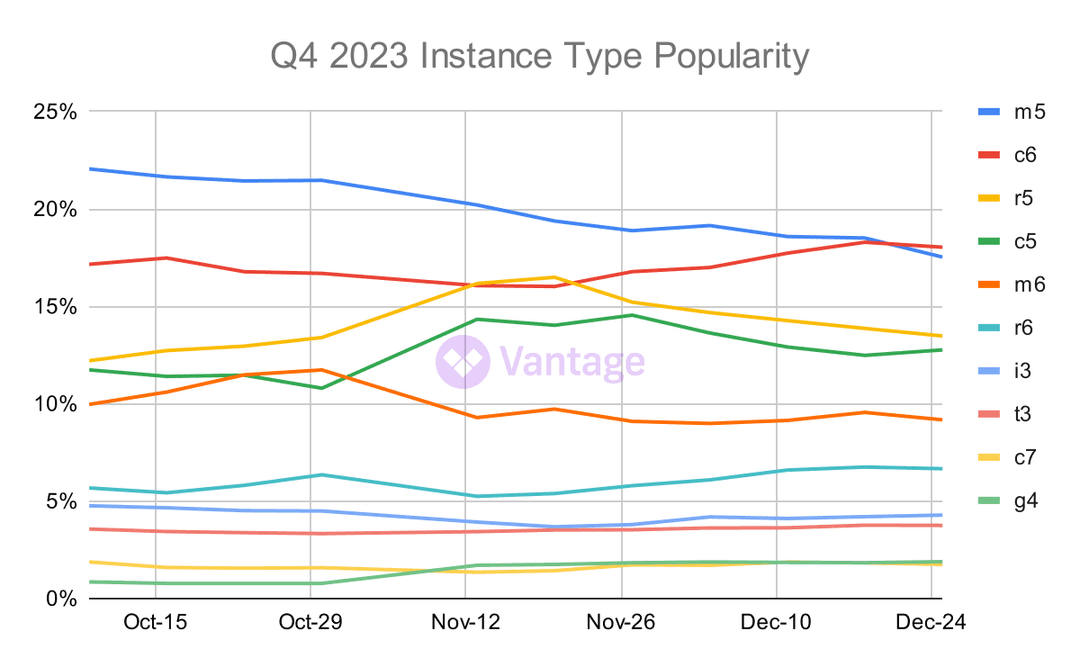
Finally, a New Generation Arises
For the first time, we are reporting that c6 instances received the most amount of spend across Vantage customers in Q4. If we reflect back to our very first cloud cost report from Q3 of 2022, c6 instances were barely visible at the bottom of the graph, while m5s had over 40% of the share of costs.
Beyond those who are overly excited by EC2 instance types, we believe this represents a full upgrade cycle for many companies. Notably, it may also represent companies shifting their architectures from x86 to arm, although this change could be spurred by recent Intel machine releases. Given that newer instance families mostly represent a better price to performance ratio, staying on top of upgrades is an important program.
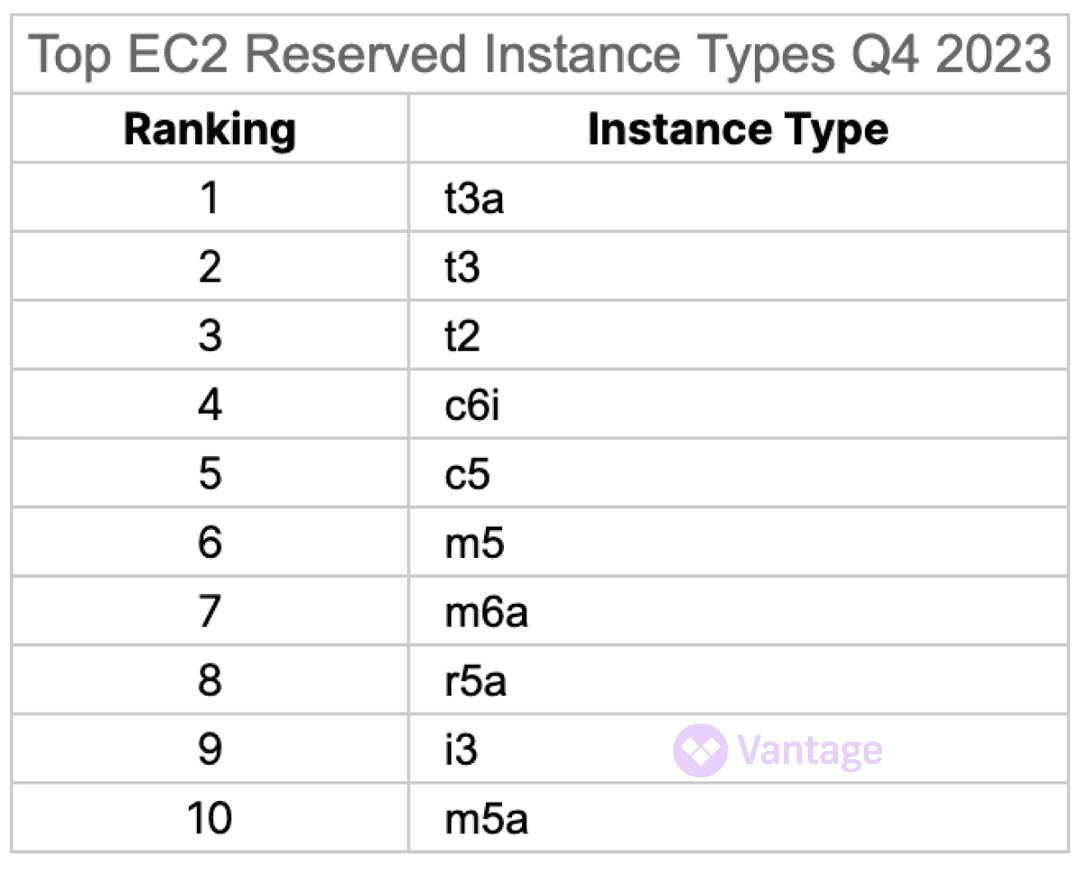
Most Popular Reserved Instance Types
So what should companies do to cope with the changes to the RI marketplace? For the first time, we are revealing the most popular RI instance types in our data.
By opting to use instance types in this list, companies can make some bets that their instance may eventually be able to be resold in the RI marketplace. At the very least, the presence of t instances in the top 3 spots indicates that companies can still make bets on many cheaper instances versus larger instances, which make a real dent in the bill.
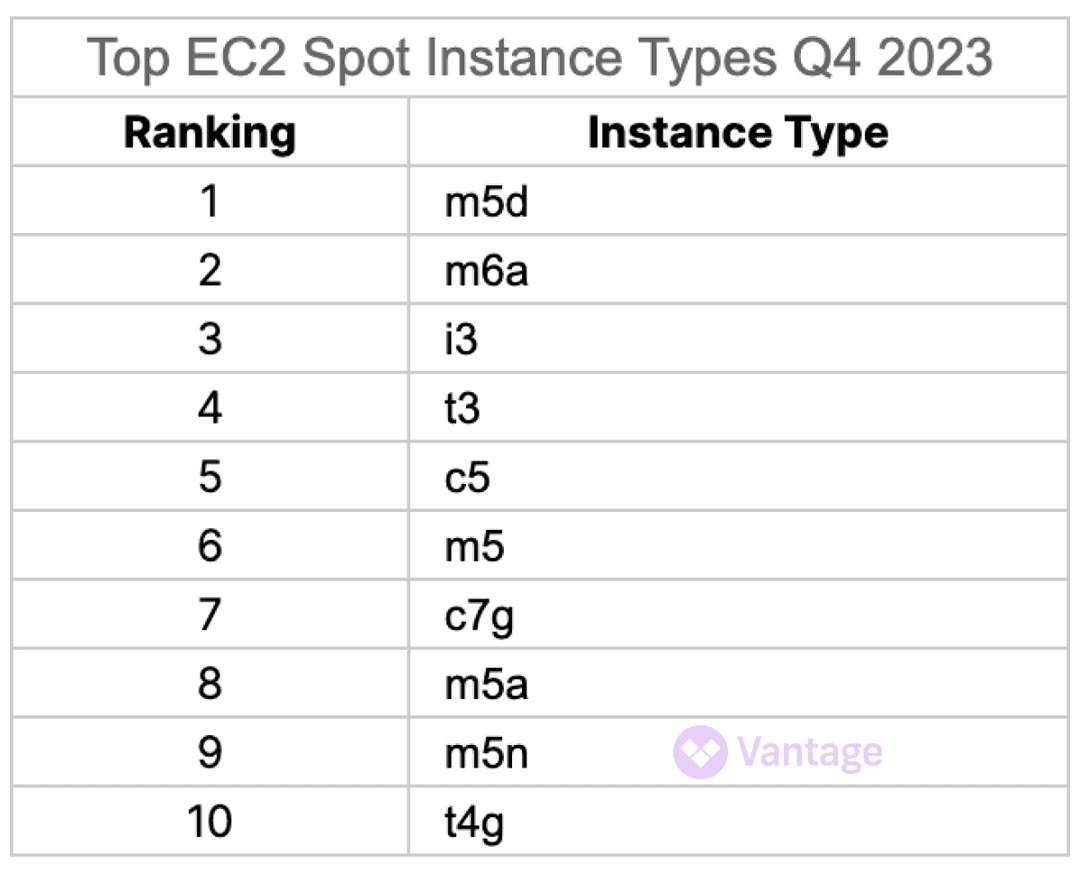
Most Popular Spot Instances
The RI marketplace is not the only discounted compute system that has seen shakeups recently. Prices were rising for spot instances as well last year.
But with spot instances, the strategy is much more straightforward. If your workload is interruptible, you can achieve very significant savings. In our data, we see that larger instances from the m series and newer instances from the c series are among the most popular instance types. Storage optimized i3's also make an appearance. To help companies choose the right spot instance, we recently added spot instance interrupt rate as a column on ec2instances.info.
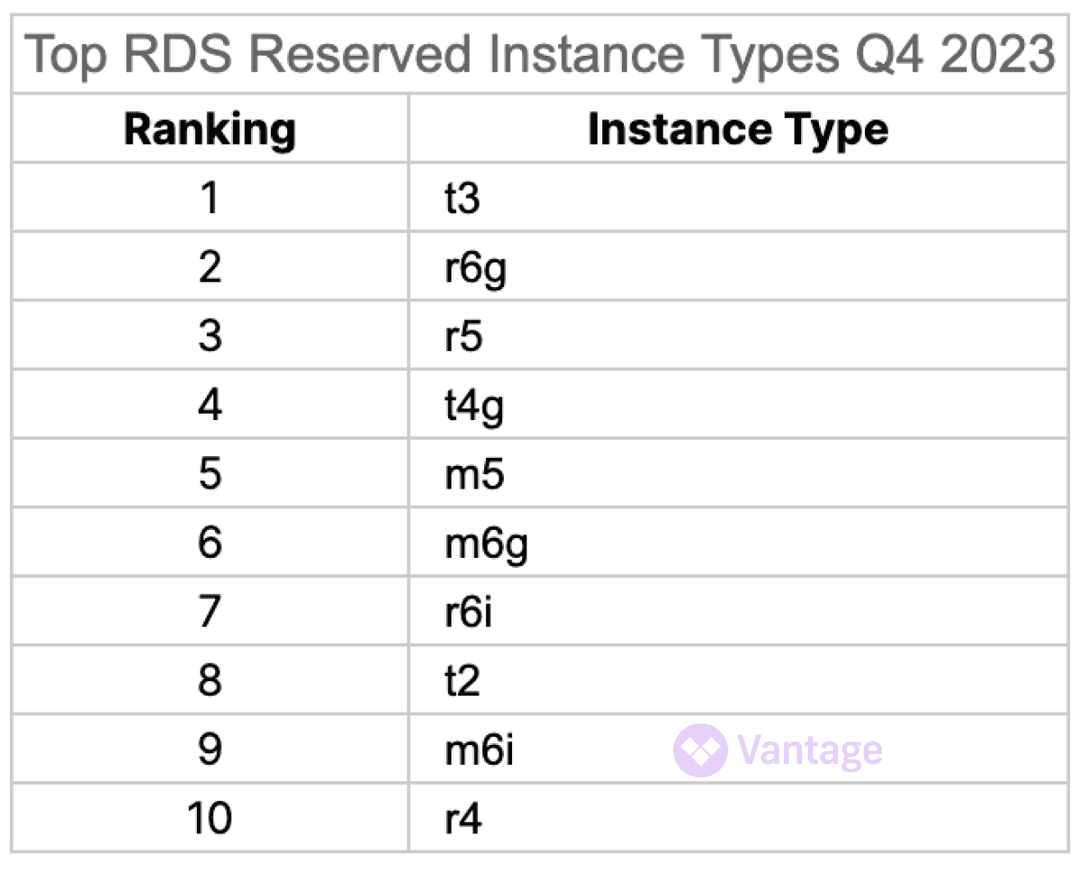
Most Popular RDS Reserved Instances
Unlike EC2, which can be covered by Savings Plans, RDS still requires Reserved Instances as the primary discounting vehicle. So which RIs are companies choosing on RDS?
Unlike EC2, we see the r instance family as being most popular on RDS. r6g and r6i are the workhorses here, and teams should feel comfortable committing to them on a 1 year or 3 year basis for their database workloads.
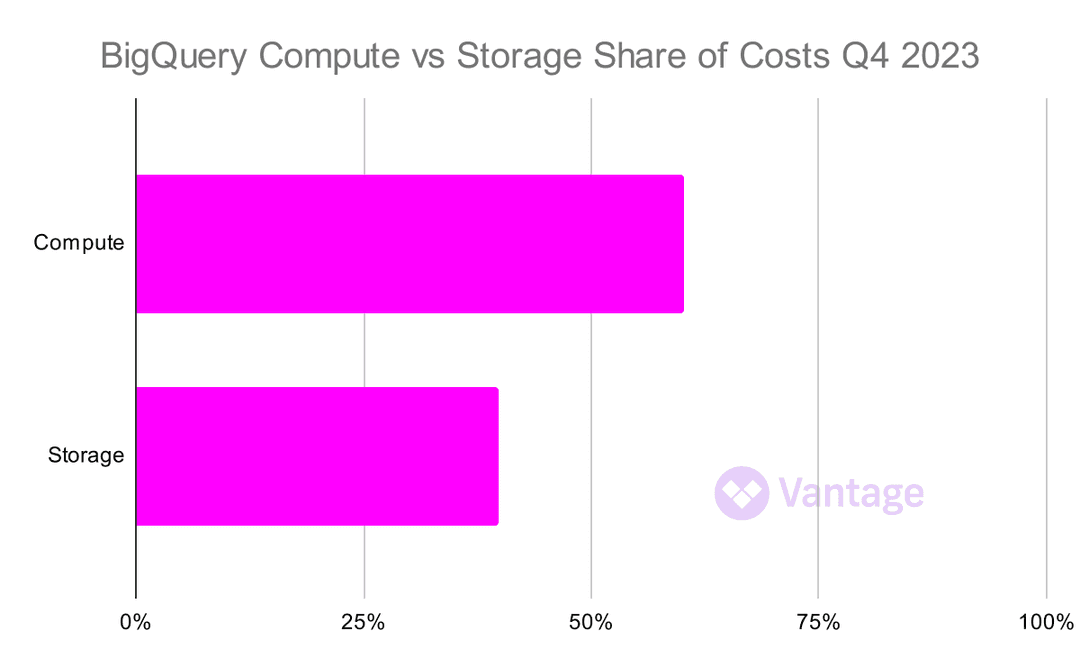
BigQuery: The Crown Jewel of Google Cloud
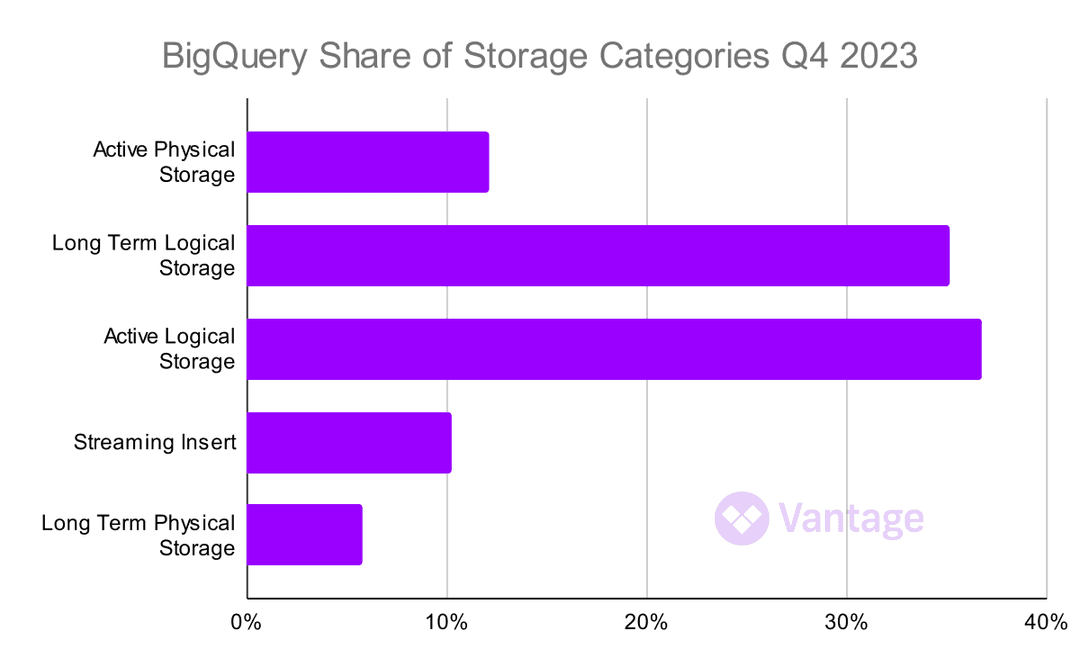
Last quarter, we covered pricing changes to BigQuery Storage. For Q4, we see a strong shift in cost breakdown towards storage costs, potentially as a result of this realignment within BigQuery's pricing structure.
Generally data warehouse costs may not be front and center for companies, but the instinct is to dump data in and never cycle it out. Given that, consider the storage class options in the next section to optimize BigQuery costs.
BigQuery Storage Classes: How to Choose?
Indeed, Google's promise to reduce physical storage costs seems to have come true. When we profiled Q3 storage, we found a relatively even breakdown of costs among storage classes. Now, logical storage leads the way, with active storage (datasets being actively queried) unsurprisingly the leader in costs. Active data engineering teams (Vantage included!) need to understand the different options and cost models, so their warehouse costs stay in line.